News and views
‘We could do more’ social enterprises tell the government

Social enterprises had plenty of ideas about the different ways they could significantly increase their positive social impact during the first evidence session of the Social, Cooperative and Community Economy All-Party Parliamentary Group (APPG)’s inaugural inquiry into the government’s commitment to grow diverse business models this week. Co-op and social enterprise leaders also listed straightforward and low or no cost barriers that the government could remove.
Peter Bundey, CEO of GLL, which operates 254 of the UK’s leisure centres, explained how supporting social enterprises would help with the government’s economic growth ambitions. “A 10% increase in our company would get 100,000 people more active and create 1000 more jobs,” he said. In terms of productivity, this could help a lot with the £138bn lost to sick days, he added. Whilst acknowledging “commendable aspiration” around social value and procurement, Bundey said progress was being held back by “conservative legal restrictions on public service procurement” and asked that the guidance and legislation that surrounds public sector commissioning is clarified.
“We need clarification so that councils can be more agile, more innovative and more prescriptive about wanting civil society organisations rather than turning to lowest cost,” said Bundey.
Peter Westall, Chief Value Officer of the Midcounties Co-op (which runs travel and childcare services as well as the familiar local Co-op shops) told the inquiry “We could do more, but the biggest challenge we face is cost pressures.”
The inquiry heard that a more unified, strategic approach to supporting the social enterprise sector was needed, with greater support, legislative reform, better access to finance, and a greater understanding of the value social enterprises bring to the economy and society.
Legislation
With revenues of £850m, 650,000 members and 6000 employees, Mid Counties Co-op made a profit of £12.4m last year but faces an increased National Insurance bill of £9.3m following changes for employers introduced in April.
Westall thought the government could help by changing ‘one size fits all’ legislation that means Midcounties Co-op face similar business rates and taxes on plastic packaging for their shops as supermarkets that operate giant stores in retail parks.
His view was echoed by Social Enterprise UK (SEUK) CEO Peter Holbrook, who asked the government to consider how tax could be used to incentivise good behaviour for businesses, particularly around business rates and corporation tax.
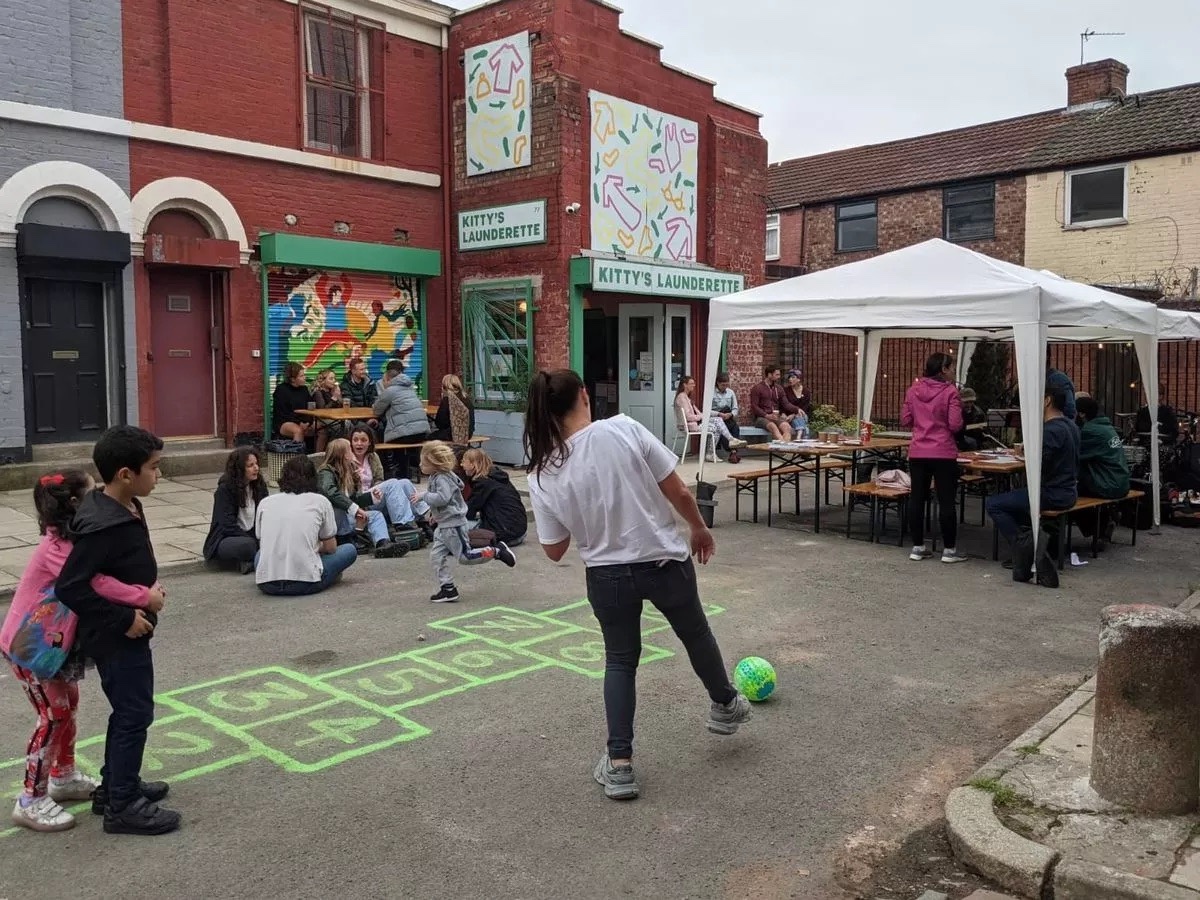
Grace Harrison, Organisational Development Lead at Kitty’s Launderette (pictured above), a coop and community hub in Liverpool, asked that community right to buy legislation be tightened up so social enterprises could find properties to operate from.
Harrison also introduced an idea she’d encountered in Italy, where legislation requires both public and private employers with more than 15 employees to hire a certain percentage of disabled people. Employers can also fulfil the quota by entering into agreements with social value organisations. “This has massively transformed the access to work opportunities for disadvantaged groups,” said Harrison.
Access to finance
Finding investment to grow remains an issue for social enterprises irrespective of size. Midcounties Co-op is one of the biggest UK childcare providers offering nearly 4000 places and Westall explained they’d like to expand this service but “as a co-op we are unable, as other business types are, to go to the city and raise funds. How do we get additional finance backing to enable us to do the things that we want to do?”. The government has established an advisory group to look at ways of mobilising social impact capital.
Jonathan Atkinson of Carbon Co-op also called for a bigger spectrum of finance options to be made available and described having limited options for using an overdraft from banks unable to assess their business risk as a social enterprise.
More grant-making startup funds were requested by Harrison, who cited a reduction in non-repayable early-stage funding sources.
Support
More awareness and practical support across the board was also requested – for local authority commissioners looking to contract social enterprises and for business support for social enterprises.
Westall also suggested that more co-op development agencies were needed, but this was challenged by Baroness Glenys Thornton who thought something broader was needed who said “this isn’t just about developing cooperatives, this is about developing social enterprises and social businesses writ large.”
Holbrook thought government officials should establish “a single vision for how cooperatives, mutuals, and social businesses can collectively recover our economy.” He suggested this might take the form of a Social Business Unit so that every government department could benefit from a level of expertise and knowledge about these diverse business models.
This was the first of four evidence sessions for the Inquiry. All the evidence presented will now be collated and incorporated into a report that will be delivered to government and other stakeholders later this year.